Herniated discs are a common spinal condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite their prevalence, many individuals remain unsure about what a herniated disc actually entails. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of herniated discs, covering everything from their causes and symptoms to various treatment options available.
What is a Herniated Disc?
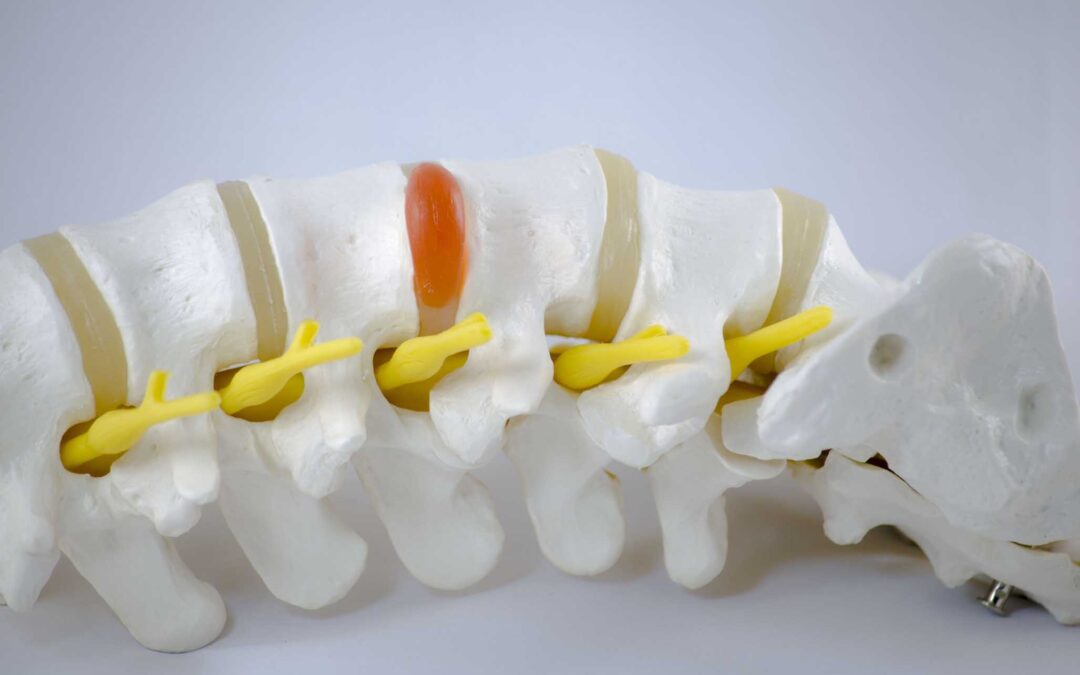
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped disc or ruptured disc, occurs when the soft, gel-like center of a spinal disc protrudes through a tear in the outer layer, known as the annulus fibrosus. This can lead to compression or irritation of nearby nerves, resulting in pain, numbness, or weakness in the affected area.
Causes of Herniated Discs:
Several factors can contribute to the development of herniated discs, including:
- Age-related Degeneration: As we age, the spinal discs gradually lose water content and elasticity, making them more prone to herniation, particularly between the ages of 30 and 50.
- Trauma or Injury: Sudden trauma or injury to the spine, such as lifting heavy objects with improper form or sustaining a fall, can cause herniated discs.
- Repetitive Strain: Engaging in activities or occupations that involve repetitive bending, twisting, or lifting motions can place excessive stress on the spinal discs, increasing the risk of herniation over time.
- Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing herniated discs due to inherited structural abnormalities or weaknesses in the spinal discs.
Symptoms of Herniated Discs:
The symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the location and severity of the herniation. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain: Sharp or dull pain that radiates from the site of the herniation to the buttocks, legs (if the herniation occurs in the lumbar spine), arms, or shoulders (if it occurs in the cervical spine).
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensations of numbness, tingling, or “pins and needles” in the affected area.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness or difficulty moving certain muscles, especially in the arms or legs.
- Changes in Reflexes: Diminished reflexes or altered reflex responses, particularly in the limbs.
Treatment Options for Herniated Discs:
The treatment approach for herniated discs typically depends on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
- Conservative Therapies: Rest, physical therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and epidural steroid injections are often recommended to alleviate pain and inflammation associated with herniated discs.
- Chiropractic Care: Spinal manipulation and manual adjustments performed by a chiropractor can help realign the spine, reduce pressure on the affected disc, and alleviate symptoms.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief or symptoms worsen over time, surgical procedures such as discectomy, laminectomy, or spinal fusion may be recommended to remove the herniated portion of the disc and stabilize the spine.
Herniated discs can cause significant pain and discomfort, impacting your daily activities and quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available, you can take proactive steps to manage your condition effectively. If you suspect you may have a herniated disc or are experiencing persistent back or neck pain, consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs. Don’t let a herniated disc hold you back from living life to the fullest – seek help and reclaim your spinal health today.
Find out more by contacting our office to schedule an appointment.
Call: 281-376-1288